Table of Contents
The Chinese electric vehicle start-up, NIO, is currently one of the most valuable automakers in the world. According to a January 2021 article by Visual Capitalist, the company has a market capitalization of around 90 billion, the world’s 5th top automaker surpassing General Motors and BMW. However, in 2019, the company was almost bankrupt. Due to this kind of turnaround, many people are considering this company the Tesla of China. In fact, the NIO’s approach to electric vehicles has led many to claim the company as a strong Tesla competitor in China.
History Of NIO
William Li, the founder of NIO, was born in 1964 in Anhui Province, China. Li studied Computer Science and Sociology as a major and law as a minor with a bachelor’s degree from Peking University. In 1998, at the age of 21, Li started his first Internet-based start-up. At that time, the Internet-based business was growing well around the world, which helped William Li to become a successful entrepreneur.
In 2000, Li started his second venture, BitAuto, with the help of his partners. By 2005, he had become the company’s CEO and chairman of the board of directors. BitAuto Holdings was listed on the New York Stock Exchange through an IPO in 2010 and the company was valued at 1 billion at the time. In 2013, Li resigned as CEO of BitAuto, and the company was sold for an undisclosed amount.

After BitAuto Holdings Ltd, in November 2014, William Li founded NextEV in Shanghai. In 2014, when the Chinese government began to focus on the expansion of electric vehicles, electric vehicle start-ups began to develop in China. William Li, who has experience in the auto industry, founded NextEV with the dream of selling electric vehicles and autonomous cars, first in the Chinese local market and later in the world market.
In addition to electric vehicle manufacturing, William Li invested in Formula E Racing in 2014 under the name Team China Racing. Although the team finished 4th in Formula-E Racing in the 2014-15 season, driver Nelson Piquet Jr. Was able to win the championship.
The Rise Of NIO
In March 2015, the company was able to raise 347 million in a Series-A funding round. In the same year, NextEV completely acquired ‘Team China Racing.’ In December 2015, Cisco veteran Padmasree Warrior was appointed as the head of the NextEV in the US division. In July 2016, NIO raised 316 million in a series-B funding round in which Sequoia Capital China, Lenovo, and several other companies invested.
In October of that year, NextEV received an “Autonomous Vehicle Testing Permit” from the California DMV. According to the permit, they will start testing vehicles on public roads as part of the autonomous vehicle program in accordance with the guidelines of the “Autonomous Vehicle Tester Program”.
According to the company, they are thinking of launching their vehicles with Level-three and Level-four autonomy. In November 2016, NextEV unveiled its first electric sports car, the NIO EP9 Sports Car, at Saatchi Gallery in London, and started branding the company as NIO.
NIO claims their first electric car to be the fastest electric car in the world, and the car set a lap record of 6 minutes, 45.9 seconds at the Nürburgring Nordschleife. Despite NIO growth, the company reported a loss of about 374 million that year, according to Statista.
In January 2017, NIO signed an agreement with Mobileye to bring Level-4 autonomy to the market by 2019. In March of that year, NIO was able to raise more than 645 million from Baidu and Tencent Holdings in the Series-C funding round.
In April 2017, NIO held 11 electric vehicle showcases at the Shanghai International Automobile Industry Exhibition and announced the launch of the ES8 electric vehicle for the Chinese market at the end of the year. In addition to this, they also started taking pre-orders for their flagship supercar NIO EP9. In November of that year, Tencent Holdings raised another 1.1 billion in a Series-D funding round.
Also in December of that year, NIO formed a Strategic Alliance with Guangzhou Automobile Group Co., Ltd, another Chinese automobile manufacturer, to manage NIO brand vehicles in R&D, manufacturing, and sales operations.

At the end of 2017, NIO’s net loss was 730 million. In May 2018, NIO launched its first battery swap station in Guangdong, China under the name “Power Swap Station”. Where only ES8 car batteries can be charged. Since its inception, NIO has sold less than 500 vehicles, and according to the company, the number of pre-orders was about 17,000.
In September of that year, NIO was listed on the New York Stock Exchange through a 1 billion IPO. On December 15 of that year, NIO launched the ES6 high-performance long-range electric SUV with a starting price of about 55,000 US dollars.
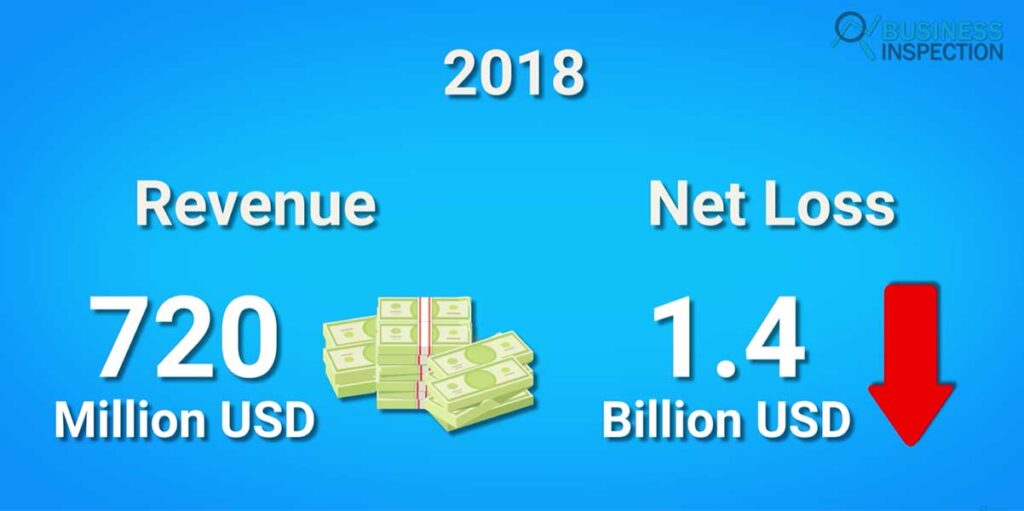
NIO also announced a 6-seater variant of the ES8 model with a starting price of around 70000 USD. In addition, as of December 15, 2018, NIO has sold a total of 9,726 ES8 SUVs and only 10 EP9s. The NIO generated 720 million in revenue in that year, but the company’s net loss was about 1.4 billion.
Why NIO Was Lagging Behind?
2018 was one of the most successful years for NIO. However, since the beginning of 2019, the company’s ES8 model SUV sales have been declining. One of the reasons behind this was the cessation of Chinese government subsidies on expensive electric vehicles and the country’s economic downturn.
In addition, the NIO had to recall 5,000 ES8 models that year due to a fire in the car’s battery. This issue with the ES8 model SUV deteriorated the business condition of the company in 2019. As a result, their newly designed Electric Sedan model also needs to be postponed. The company also has to scrap its plan to set up NIO’s car manufacturing plant in its own factory in Shanghai.
Instead of setting up its own manufacturing plant, NIO, as before, started manufacturing its electric vehicles from JAC Motors. The economic situation became so bad that at one point NIO was forced to sell their All-electric racing series Formula E team.
In the wake of all this, the NIO has to go through major cost-cutting efforts throughout the year. At the beginning of 2019, the total number of employees in the company was about 10000. Due to the economic downturn, in 2019, along with China, NIO’s Silicon Valley office had to lay off employees in three phases.
The situation was so bad that the company was forced to close its San Francisco operations as well. NIO had to lay off more than 2,000 employees worldwide that year, and by the end of the year, the company had a total workforce of less than 7,500.
In addition to layoffs, the company had to go through marketing-related cost-cutting efforts, and these major cost-cutting efforts eventually reduced their operating expenses from 396 million in the second quarter to 306 million in the third quarter. According to NIO’s Annual Financial Report, the company was able to deliver 20,565 ES8 and ES6 vehicles last year, with total revenue of 1.12 billion USD.
Despite the continuous cost-cutting effort, the company’s net loss in 2019 was 1.62 billion USD. According to an article by Verge, the company has had to calculate a loss of 6 billion from its inception in 2014 to December 2019.
Meanwhile, when the coronavirus pandemic virus started in China at the end of 2019, the country went into lockdown. As a result, NIO’s sales volume declined and the company almost reached the brink of bankruptcy. As a result of the shortage of liquidity to continue operations at one stage.
Turnaround Strategy Of NIO
In the wake of NIO’s financial situation, on February 25, 2020, the municipal government of Hefei, Anhui Province, China, announced a 1.4 billion investment in the company. This investment by the Hefei municipal government has resulted in the creation of a new organization called Nio China, which will be headquartered in Hefei.
There will be a new manufacturing center as well as all NIO China-based activities will be restructured in NIO China. Also on the same day, NIO’s next electric vehicle smart electric coupe SUV EC6 will start production, said the company’s CEO William Li. In April of 2020, NIO China received another 1 billion in funding from state-controlled Hefei Construction Investment Holding Co Ltd, CMG-SDIC Capital Management Co Ltd, and Anhui High and New Technology Industrial Investment Co Ltd.
This funding was significant during the company’s recession. NIO’s EC6 Smart SUV was launched in July of that year. In August of that year, Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL), Hubei Science Technology Investment Group Co. Ltd., and through a subsidiary of Guotai Junan International Holdings Limited, NIO launches their new service Battery as a Service (BaaS).
In addition to all this, the NIO was delivering their electric car at a regular rate. Combining all those, investors regained confidence in the NIO and the company’s stock price began to rise steadily. On November 25, the price rose to 57 per share. The company has a market capitalization of 73.6 billion. The company currently has a market capitalization of about 80 billion and is the world’s 5th top auto car manufacturer in terms of valuation.

According to the NIO’s annual report, the company delivered more than 17,000 vehicles in the fourth quarter of 2020, a record for the NIO. That year, the company delivered about 44,000 electric vehicles. The company’s revenue from vehicle sales was 2.3 billion USD. On the other hand, the total revenue of the company in 2020 was about 2.5 billion USD.
NIO also declared its first profit in 2020 since its inception in 2014. In 2020, the company was able to generate more than 287 million in profits. In January 2021, NIO unveiled the all-electric sedan ET7. The car is NIO’s first sedan model and Autonomous Driving.
With the ET7 model sedan, the company is now in direct competition with the popular models of US-based Tesla INC. As a result of such a turnaround of the company, industry analysts think that in the future, the company will be able to position itself as a strong competitor to Tesla in China.










Leave a Comment