Table of Contents
In terms of popularity, football is at the top of the world’s top sports, with 4 billion fan-followers. And, the most popular and wonderful event of this sport is the FIFA World Cup, which is held every four years with the football team of the qualified countries. The event, known as The Greatest Show on Earth, is so popular that during the Russia World Cup, a total of 3.26 billion people worldwide enjoyed the play on TV. In addition, the total audience in that World Cup was about 3.57 billion.
However, to implement the entire event in this World Cup host country, the stadium or renovation needs to invest a lot of time and money to develop infrastructure, communication, transportation, accommodation, and hospitality services. For example, the country is spending more than $200 billion to host the 2022 Qatar World Cup. Why is Qatar spending this amount of money to host the FIFA World Cup, and how will it be economically for the country?
Overview
Starting in November 2022, the 22nd FIFA World Cup is being hosted by Qatar, the only Muslim country to host FIFA World Cup ever. As the host country for FIFA World Cup 2022, Qatar was selected 12 years ago. The host country for the FIFA World Cup is determined by bidding officials of soccer’s governing body, FIFA, at least 8 to 10 years before the World Cup, especially stadiums and other infrastructural issues.
The host country needs to build stadiums as per FIFA guidelines and hotels, transportation, and communication facilities following FIFA instructions to accommodate FIFA officials, players, and fans. Naturally, countries that host various types of club football, leagues, and international matches almost year-round, get more preference as they have readymade establishments to fill up FIFA’s requirements where some additional upgradation and maintenance will let them host the FIFA World Cup.
But, countries that do not host football events on a regular basis require considerable time to fulfill FIFA’s infrastructure, communication, and transportation-related requirements. That is why the host country is decided so many years before the World Cup is held.

In 2010, it was decided which countries would host the FIFA World Cup in 2018 and 2022. England, Russia, Belgium, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain all put in bids to host the 21st World Cup in 2018. Belgium and the Netherlands put in a bid together, and Portugal and Spain put in a bid together. On the other hand, Australia, Japan, Qatar, South Korea, Indonesia, Mexico, and the USA all put in bids to host the 22nd World Cup in 2022. After a full bidding session on December 2, 2010, FIFA chose Russia to host the 2018 World Cup and Qatar to host the 2022 World Cup.
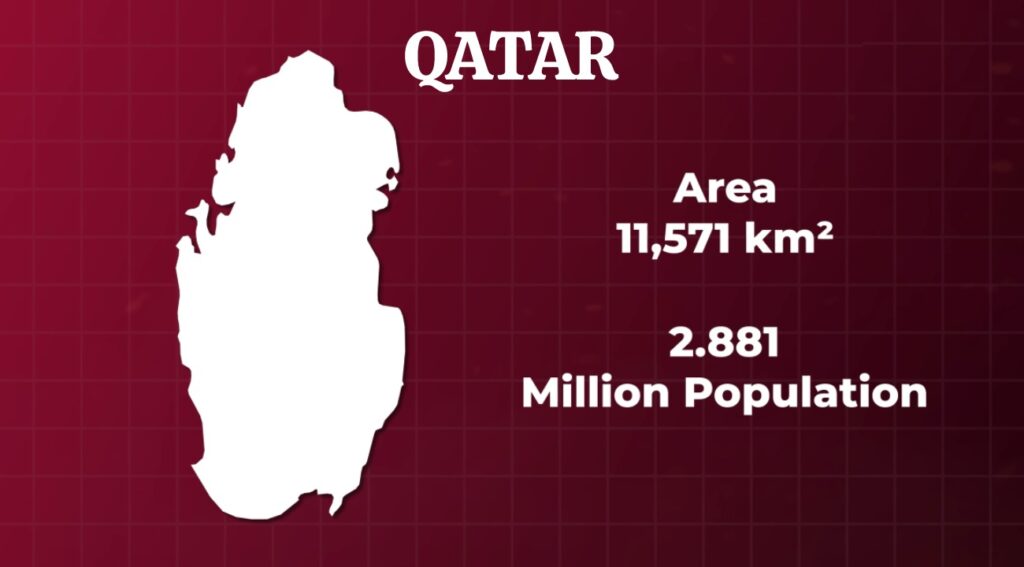
But the process by which Qatar was chosen as the host country was controversial from the start. Why is Qatar, a Middle Eastern country with less than 3 million people and an area of only 11,000 square kilometers, hosting the World Cup? It is the smallest country in the world to host the FIFA world cup. Also, Qatar isn’t a football superpower.
In fact, the country hasn’t been able to qualify for any of the last 21 World Cups. In 2022, as the host country, Qatar will be able to play in the World Cup for the first time. Also, the FIFA World Cup is held in June and July, which is the summer, when other leagues and football events around the world are not going on. In the Middle East, Qatar is a desert country where July temperatures average up to 42 degrees Celsius, which is too hot for most people to live in.
Because of this, the 2022 World Cup has been moved to November, during the winter. Because of this, the World Cup schedule clashed with the schedules of other football leagues around the world. As a result of these scandals, two members of FIFA’s executive committee lost their voting rights. They were accused of using their voting power to get bribes from candidate countries for the right to host the World Cup.
According to The Athletic, 15 of the 22 people on FIFA’s executive committee, including Ex-FIFA president Sepp Blatter, voted for Qatar to host the 2022 World Cup. Most of these people had been banned from all FIFA activities for various types of corruption. Even so, Qatar is working hard to host the 2022 World Cup of football, which will begin in November, and the country is spending a total of 220 billion dollars on this.
The Economy of the FIFA World Cup
Since FIFA arranges the accommodation and hospitality for the players and staff of the 32 teams, FIFA officials, and referees, and looks up to new football technology, and all kinds of logistics, the organization has to spend billions of dollars behind each World Cup. FIFA has its own investment budget for each World Cup.
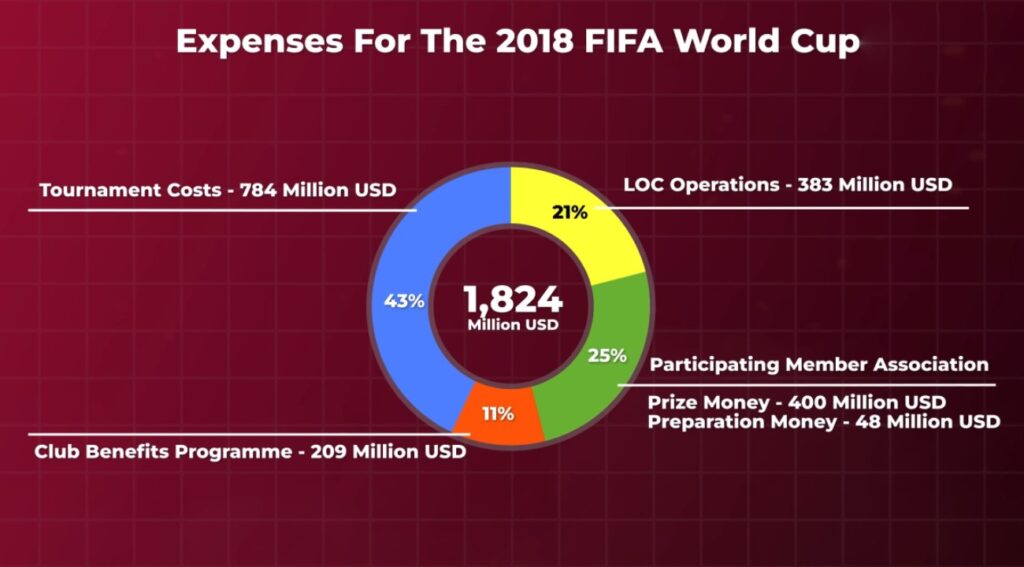
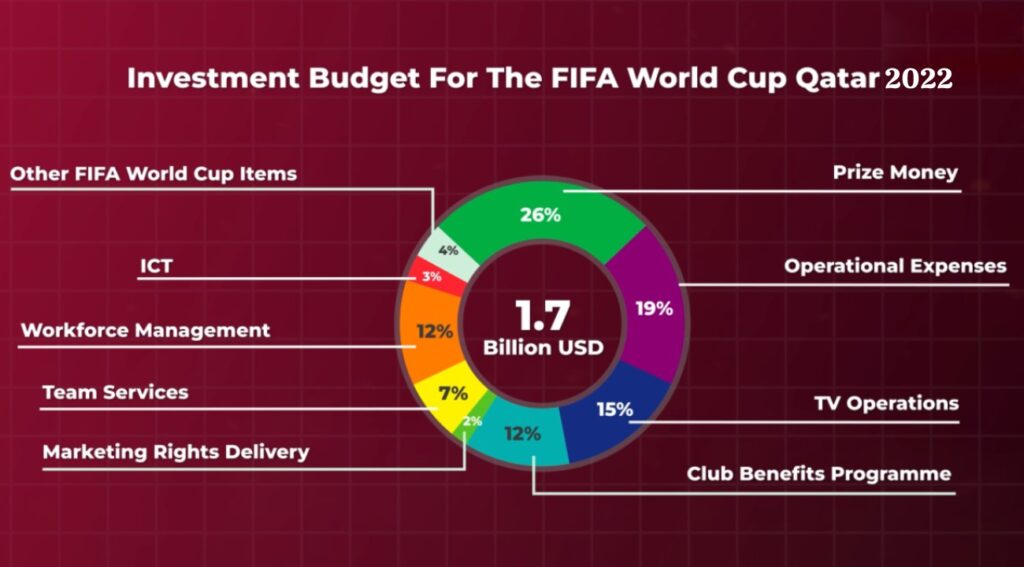
FIFA’s total investment budget for the 2018 World Cup in Russia was $1.95 billion, with a total expenditure of $1.8 billion. Within this budget, Tournament costs were 784 million dollars, 400 million dollars were provided to participating member associations, 209 million dollars for Club Benefits Program, and 383 million dollars were provided to the Local Organizing Committee or LOC. On the other hand, FIFA has set a total investment budget of $1.7 (1.69) billion for the 2022 World Cup in Qatar. However, the amount paid to the Local Organizing Committee in this World Cup has not yet been disclosed.
To host the World Cup, the host country has to spend a lot of time and money building or renovating stadiums and developing transportation and housing infrastructure, as well as meeting FIFA’s requirements and making sure the event runs smoothly. To host the World Cup, there must be at least 8 to 12 stadiums that can hold between 40,000 and 80,000 people. But the number of people a stadium can hold depends on what kinds of games are played there.
For example, the World Cup stadium where the opening ceremony will be held must be able to hold at least 80,000 people. Also, the stadiums that will host the semi-finals must be able to hold at least 60,000 people. But starting with the 2026 World Cup, the number of teams that can compete will go from 32 to 48, and FIFA will require 14 stadiums.
In terms of transportation, FIFA says that every stadium must have an airport that can handle at least 1,450 people per hour. FIFA requires at least 1,760 to 8,080 hotel rooms for spectators in each host city, as well as 72 base camp hotels for teams and referees and 4 hotels for each stadium location.
Although Qatar is not a superpower in football and neither of its football clubs is as popular as European clubs, the country had to develop its infrastructure as per FIFA’s requirements. Therefore, the country has to invest a lot of money. According to a CNBC source, Qatar is spending a total of $220 billion to host the FIFA World Cup in 2022, which is more than 60 times more than the $3.6 billion spent on the 2010 FIFA World Cup, hosted in South Africa.
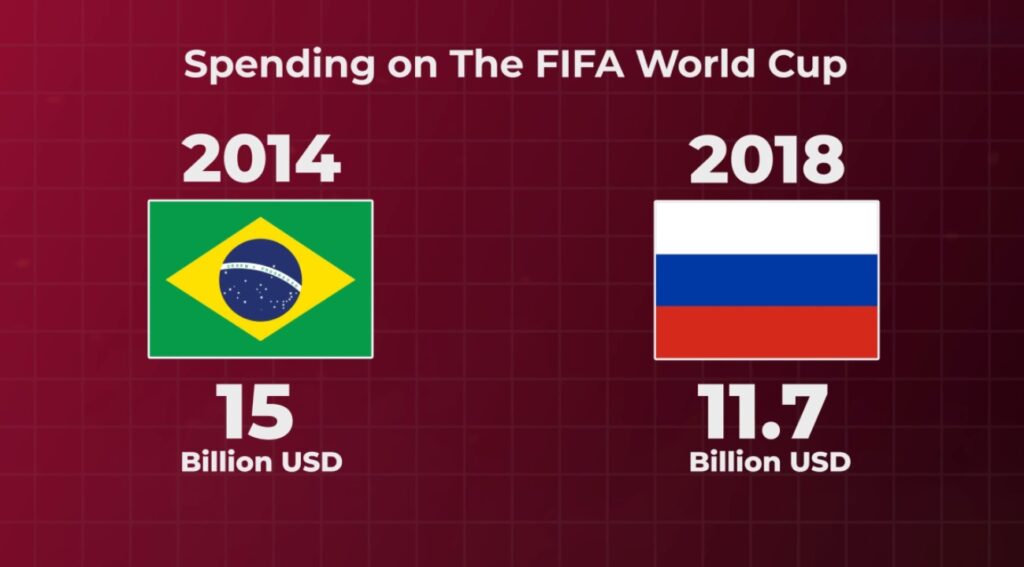
On the other hand, Brazil and Russia spent $15 billion and $11.7 billion, respectively, on the 20th and 21st editions of the World Cup in 2014 and 2018. According to a Statista report, of the total $11.7 billion Russia spent on hosting the 2018 World Cup, $6.11 billion was spent on transportation infrastructure, $3.5 billion on sports facility construction and reconstruction, and $680 million on accommodation facilities infrastructure development.

Qatar is one of the oil-rich countries in the Middle East. However, like other Middle Eastern countries, Qatar is trying to diversify its oil-dependent economy. Among these, Dubai in the United Arab Emirates has already established itself as a tourist destination and business hub, and Saudi Arabia is also trying to follow the same path.
Qatar is already a transportation hub, and the country is trying to promote itself globally as a tourist destination by hosting the World Cup in 2022 in the future, it’s trying to establish itself as a tourism and business hub. In view of this, most of the country’s infrastructure projects for hosting the World Cup are being developed in line with the country’s future Qatar 2030 National plan. The country has spent $6.5 billion to $10 billion on building the stadiums for the World Cup, and the rest of the 220 billion dollars is being spent on various transportation infrastructure and innovation centers in the country.
For example, since 2014, the country has spent a total of $16 billion to increase the passenger handling capacity of the operational Hamad International Airport from 30 million to 50 million. In addition, the Doha Metro system has been built to facilitate fast travel to various parts of the city for fans arriving for the World Cup and tourists visiting Qatar in the future, which cost $36 billion. Apart from this, Qatar has invested $45 billion to build Lusail city, an entirely new city, in addition to building 100 new hotels, hospitality centers, and shopping malls to provide proper accommodation for audiences and tourists during the World Cup season and beyond.

Although Qatar has already spent a lot to host FIFA World Cup 2022, the country has seen a vast amount of infrastructure and communication development which is likely to be very fruitful for the country’s economy in the future. Multinational companies which have not established their business in Qatar due to a lack of proper infrastructure will now be interested in running their operations there.
In addition, a large number of tourists will visit the country during and after the World Cup, which will greatly increase the growth of Qatar’s tourism industry. According to a Bloomberg report, Qatar will be able to attract 1.2 million visitors to the 22nd edition of the FIFA World Cup, which starts in November. On the other hand, according to a source from The Athletic, FIFA authorities have already received 1.2 million ticket requests within 24 hours of the World Cup ticket sales in January 2022. In addition, the World Cup is expected to add another $17 billion to the country’s economy.










Leave a Comment